Factors to be considered while selecting diaphragm pump are as follows:
Fluid – One of the most important factors that needs to be
taken into consideration is the Type, Composition & Nature of the fluid in order to avoid
corrosion of wetted parts & also to prevent the wear & tear of the pump. It is also
necessary to determine - What’s the chemical composition of the fluid? What’s the consistency?
Is it a slurry (thick suspension of solids in liquids), or is it a clean fluid?
1. Nature of fluid:
- Corrosive fluids: Corrosive fluids like sulfuric acid,
Nitric acid, Sodium hydroxide etc. generally destroys & damages the material when comes
in contact. So a careful selection for the wetted part & diaphragm is needed.
- Abrasive Fluids: Abrasive fluids like paints, inks,
ceramic slurry etc. which contains solid particles that can damage the contact material by
scraping or wearing. For example, for paints we can use PTFE Diaphragm & SS316 as the
wetted material.
- Toxic Fluids: Toxic fluids like lead, mercury etc. has
the quality of being toxic or poisonous. Diaphragm pumps are seals-less & have leak free
design hence they are suitable for such liquids.
- Flammable Fluids: Flammable chemicals like acetone,
benzene, petroleum etc. that easily catches fire. Therefore AODD pumps are used as they are
air driven & intrinsically safe. However, some liquids may generate a static charge, so
pump should be completely grounded. We recommend using Antlia Pumps for such applications.
- Shear Sensitive Liquids: Liquids like tomato ketchup,
emulsions, curd, paste, etc when subjected to shear (or churning), can change the product
characteristics. Some liquids are shear thinning, some are shear thickening. Since Diaphragm
pumps run at lower speed, they are ideal for such liquids. We recommend running the pump at
a slower speed than normal for such applications.
- Vapour Pressure: Liquids such as diesel, hydrocarbons
have low vapour pressure. We need to ensure that such pumps run at low speed & also the
suction lift is limited, otherwise the AODD pump may not be able to deliver required flow.
2. Viscosity – Viscosity is resistance to the flow. In
other words, we can say it the stickiness of the fluid. It is important to determine how viscous
the liquid is. Depending on the viscosity & frictional losses in the pipeline pump size
needs to be determined.
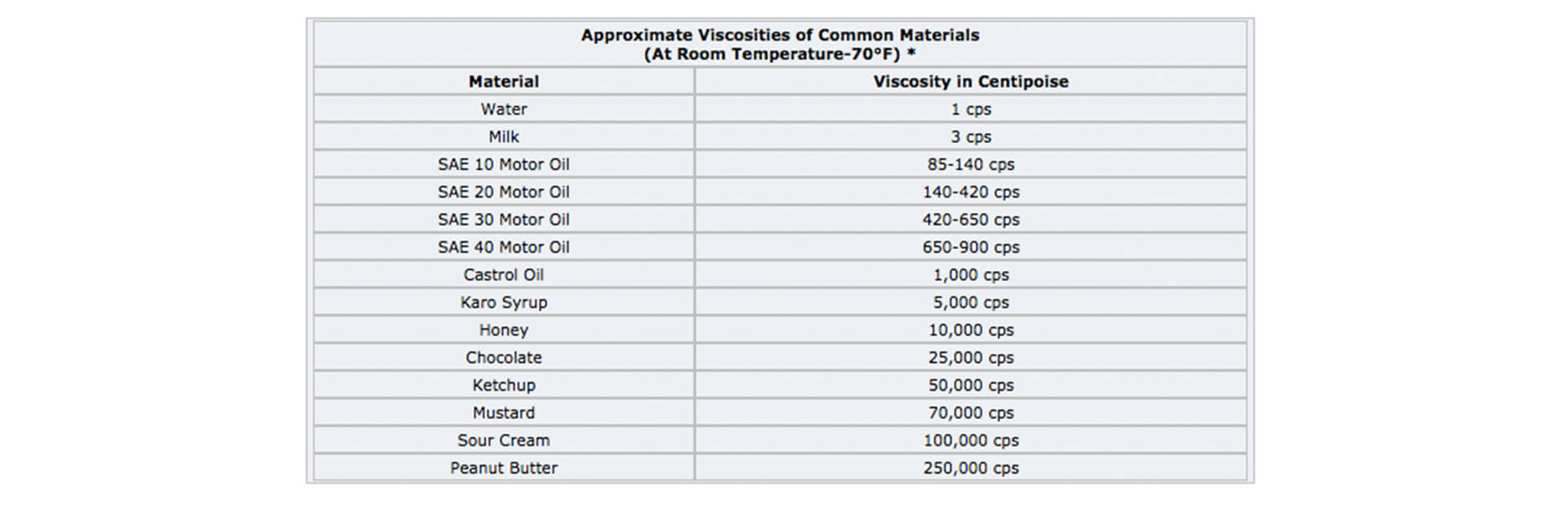
For example, it is better to use 1.5” or 2” size diaphragm pumps for liquids above 5000 cps
depending on the head.
3. Pressure Determining the pressure conditions at the
suction(Inlet) & discharge(outlet) will help to select the appropriate double diaphragm pump
size.
- Suction Pressure: Simply it is the pressure at the
Inlet of the pump. AODD pump can work on both flooded suction as well as suction lift
conditions as they are self-priming. It is also important to determine if high suction
pressure is there, as it may hamper the lifting of the suction valves affecting pump
performance.
- Discharge Pressure: It is the head requirement at the
discharge of the pump. It is also known as delivery pressure i.e. at what height the
fluid/liquid has to be delivered along with frictional losses in the pipeline.
4. Flow Rate – To select the size of the diaphragm pump,
the flow rate is considered at first. For higher flow rate one can select the larger pump with
larger port sizes i.e. Suction & Discharge connection & vice versa. It can be measured
in LPM or GPM or m3/hr.
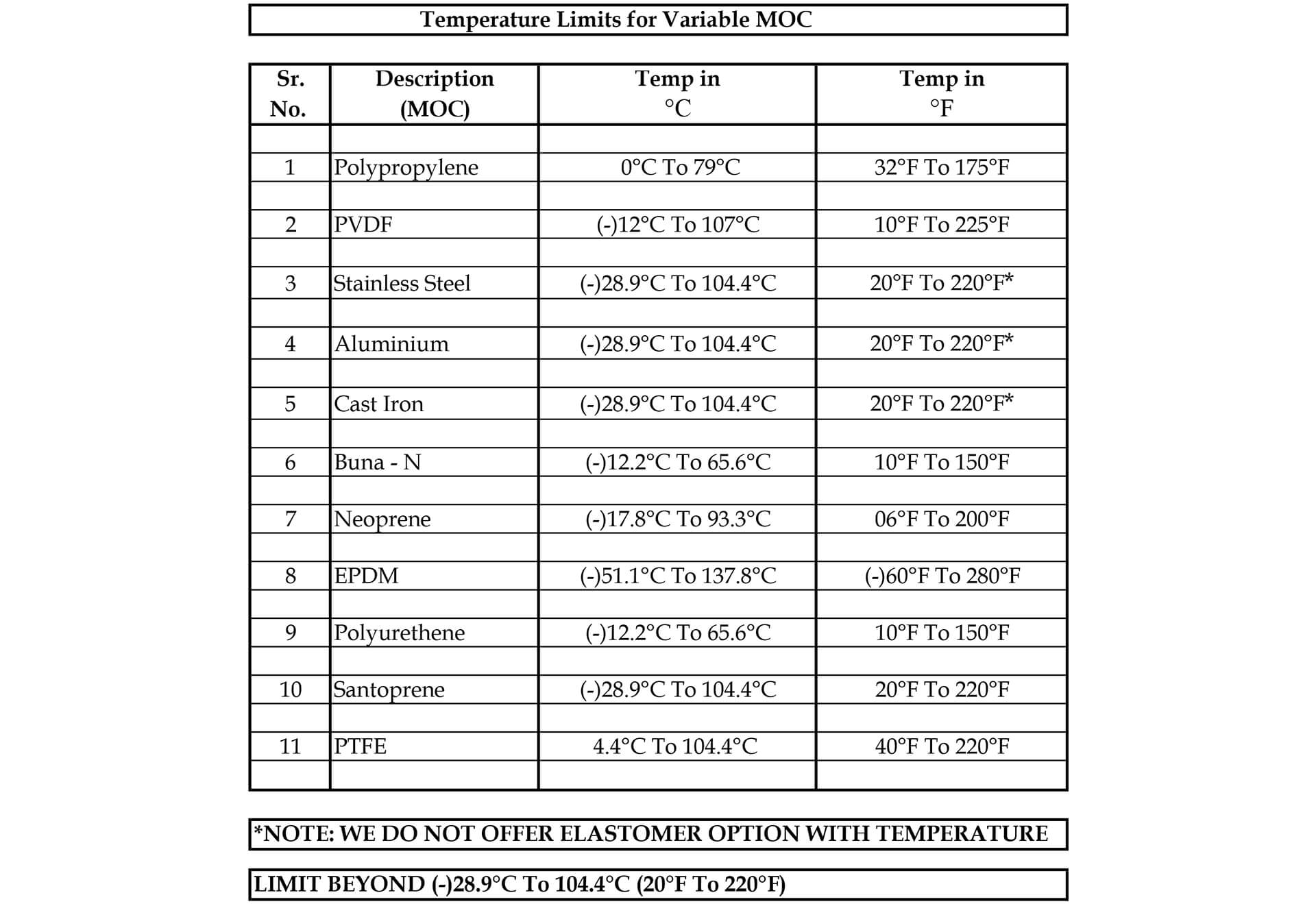
5. Temperature – Pump materials have temperature
limitations. We must know the operating temperature as well as ambient conditions to ensure that
diaphragm pump material is best suited for a particular application. For example, Santoprene
diaphragms are limited to or less than 104.4°C.
6. Service – AODD Pumps can be used for continuous as well
as Intermittent application. Mainly used for Unloading & Transfer Purpose, air pumps are
simple to operate & they can also be mounted on a movable trolley so that it can be easily
used at the required place whenever needed with a proper availability of compressed air.